Kingdom Animalia- Kingdom Animalia is also called as Metazoa
- Does not contain the prokaryotes or the protists - All members of Animalia are multicellular and heterotrophs (rely directly or indirectly on other organisms for their nourishment) - Most of the K.Animalia ingest and digest food in their internal cavity - Animal cells lack the rigid cell walls that characterze plant cells - Bodies of most animals are made up of cells organized into tissues and each tissue is further organized into specialized organs - Most Animals are capable of complex and relatively rapid movement compared to plants and other organisms - Most Animals reproduce sexually - Most Animals are diploid - Between 3 to 30 million species of animals inhabit in the Earth, only a rough estimate could be made - Range in size from microscopic animals such as plankton to massive blue whales. - Largest subgroup of animals is the insects - Animals are thought to have evolved from flagellate protozoa and the oldest animal fossils date back 600 million years, to the latter part of precambrian. - Most major groups of animals evolved during the Cambrian period |
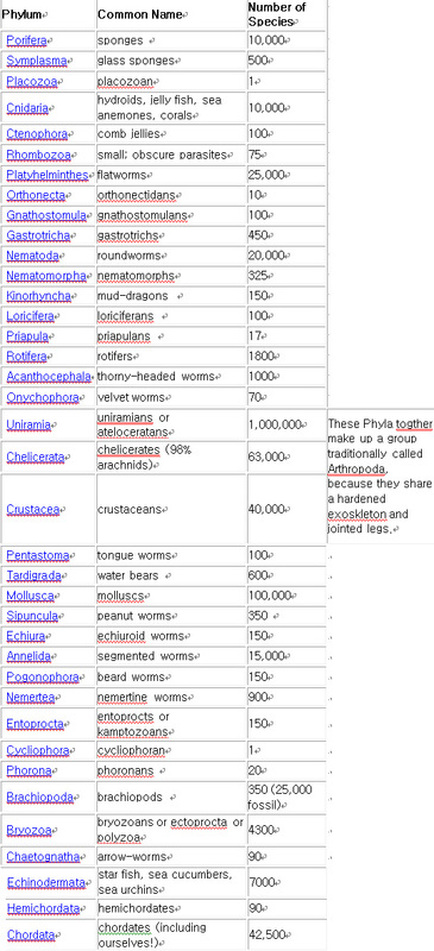
Phyla of Kingdom Animalia |
Example of Kingdom Animalia - Canis lupus familiaris

Domain- Eukarya
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Chordata
Subphylum-Vertebrata
Class- Mammalia
Order- Carnivora
Family- Canidae
Genus- Canis
Species- Canis lupus
Subspecies- Canis lupus familiaris (Dog)
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Chordata
Subphylum-Vertebrata
Class- Mammalia
Order- Carnivora
Family- Canidae
Genus- Canis
Species- Canis lupus
Subspecies- Canis lupus familiaris (Dog)
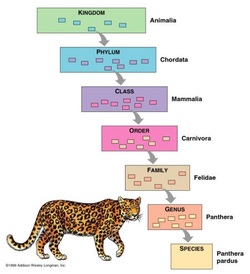
Example of Kingdom Animalia - Felis catus

Kingdom - Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Felis
Species - Felis catus (House Cat)
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Carnivora
Family - Felidae
Genus - Felis
Species - Felis catus (House Cat)
Example of Kingdom Animalia - Orcinus orca

Kingdom - Animalia
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Cetacea
Family - Delphinidae
Genus - Orcinus
Species - Orcinus orca (Killer Whale)
Phylum - Chordata
Class - Mammalia
Order - Cetacea
Family - Delphinidae
Genus - Orcinus
Species - Orcinus orca (Killer Whale)
Summary of K.Animalia
Characteristics of Animalia Kingdom:
- Eukaryote
- Multicellular
- Heterotrophic
- Terrestrial and Aquatic
- Sexual ( a few asexual)
- Motile ( a few are nonmotile)
Examples: sponges, jellyfish, mollusks, round worms, flat worms, segmented worms, arthropods, starfish, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals