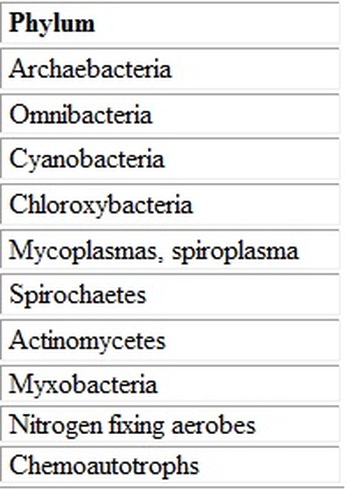
Kingdom Monera- Comprised of 2 subkingdoms: Archaeabacteriobion & Eubacteruaibionta
- Prokaryotic; single-celled with no nucleus - Bacteria - Both Autotrophs and heterotorphs - Roles in oceans: base of food chian, converters of nitrogen gas into useful forms for organisms, decomposers. - Organisms in the Kingdom Monera lack nuclei and organelles and most of their cell walls are made up of peptidoglycan (except archaebacteria) - Most organisms in K.Monera uses flagella for movement - Digestion is done extracellular(outside the cell) and nutrients are absorbed into the cell - Saprophytes is a special kind of heterotroph, obtain energy by feeding on decaying matter - Some bacteria live in symbiotic relationships with other organisms, parasitism (harmful to the host), commensalism (one organism benefits while the other is unaffected), and mutualism (both organism benefits) - Reproduce through binary fission (asexual) or conjugation (sexual) |
Example of Kingdom Monera - Escherichia coli
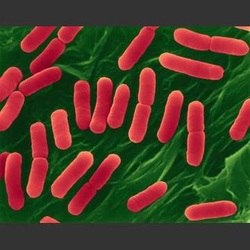
Kingdom: Monera (Bacteria)
Phylum: Proteobacteria
Class: Gammaproteobacteria
Order: Enerobacteriales
Family: Enterobacteriaceae
Genus: Escherichia
Species: Escherichia coli
Example of Kingdom Monera - Bacillus anthracis
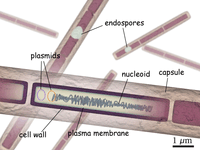
Kingdom: Monera (Bacteria)
Phylum: Firmicutes
Class: Bacilli
Order: Bacillales
Family: Bacillaceae
Genus: Bacillus
Species: Bacillus anthracis
Phylum: Firmicutes
Class: Bacilli
Order: Bacillales
Family: Bacillaceae
Genus: Bacillus
Species: Bacillus anthracis
Example of Kingdom Monera - Helicobacter pylori
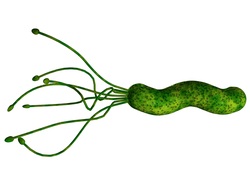
Kingdom: Bacteria
Phylum: Proteobacteria
Class: Epsilonproteobacteria
Order: Campylobacterales
Family: Helicobacteraceae
Genus: Helicobacter
Species: Helicobacter pylori
Phylum: Proteobacteria
Class: Epsilonproteobacteria
Order: Campylobacterales
Family: Helicobacteraceae
Genus: Helicobacter
Species: Helicobacter pylori
Summary of K.Monera
Characteristics of the Monera Kingdom:
Example: bacteria - both eubacteria (True bacteria) and archebacteria (ancient bacteria)
- Prokaryotes
- Heterotrophic and autotrophic
(Heterotrophic - Organism that can't synthesize (make) it's own food)
(Autotrophic - Organism that CAN make it's own food - photosynthesis) - Anaerobic and aerobic respiration
- aquatic, terrestrial and in the air
- mostly asexual
- mostly non motile (1 form does move)
Example: bacteria - both eubacteria (True bacteria) and archebacteria (ancient bacteria)