Kingdom Protista- Mostly Unicellular, Some are multicellular (algae)
- can be both heterotrophic or autotrophic - Mostly living in water (some live in moist soil or in human body) - ALL are eukaryotic, simplest of the eukaryotes - Protista = "The very first" - Unusual group of organisms put together because they don't really seem to belong to any other group. - Home for 'leftover' organisms - Both micro and macroscopic |
The protozoa:
Phylum Ciliophora (8,000 sp.,) Blepharisma, Paramecium Phylum Sarcodina (over 300 sp.) - Amoeba, radiolaria, foraminifera Phylum Sporozoa (3,900 sp.) - Plasmodium The algae: Phylum Phaeophyta (1,500 species, fr. Greek phaios = brown) - Fucus Phylum Rhodophyta (fr. Greek rhodos = red, 4,000 sp.) - Polysiphonia Phylum Bacillariophyta (11,500 sp., many more fossil sp., fr. Latin bacillus = little stick) - diatoms Phylum Euglenophyta (800 sp.) - Euglena Phylum Pyrrophyta (3,000 sp., fr. Greek dinos = whirling, Latin flagellum = whip) - dinoflagellates, Ceratium Phylum Chlorophyta (7,000 sp., fr. Greek chloros = yellow-green) - Volvox, Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas |
Example of Kingdom Protista - Coleps amphacanthus

Domain: Eukaryota
Kingdom: Protozoa
Subkingdom: Biciliata
Infrakingdom: Alveolata
Phylum: Ciliophora
Subphylum: Intramacronucleata
Class: Ciliatea
Order: Gymnostomatida
Family: Colepidae
Genus: Coleps
Specific Descriptor: amphacanthus
Scientfic Name: Coleps amphacanthus
Kingdom: Protozoa
Subkingdom: Biciliata
Infrakingdom: Alveolata
Phylum: Ciliophora
Subphylum: Intramacronucleata
Class: Ciliatea
Order: Gymnostomatida
Family: Colepidae
Genus: Coleps
Specific Descriptor: amphacanthus
Scientfic Name: Coleps amphacanthus
Example of Kingdom Protista - Paramecium caudatum
Kingdom: Protozoa
Phylum: Ciliophora
Class: Ciliatea
Order: Hymenostomatida
Family: Parameciidae
Genus: Paramecium
Species: Paramecium caudatum
Phylum: Ciliophora
Class: Ciliatea
Order: Hymenostomatida
Family: Parameciidae
Genus: Paramecium
Species: Paramecium caudatum
Example of Kingdom Protista - Stemonitis fusca

Scientific Name: Stemonitis fusca
Common Name: Slime mold
Summary of K.Protista
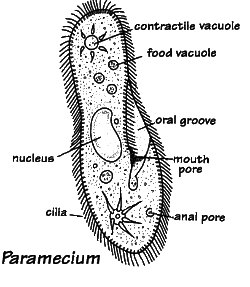
Characteristics of the Protista Kingdom
Example: Protozoa, slime molds and algae
- Eukaryotes
- Heterotrophic and Autotrophic
- Unicellular
- Mostly aquatic
- Mostly asexual
- Motile and nonmotile
Example: Protozoa, slime molds and algae
